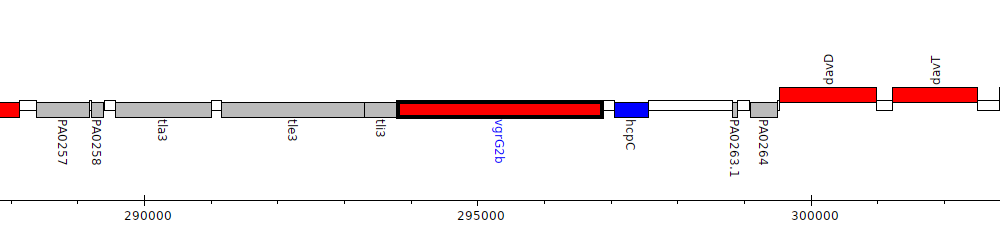
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, PA0262 (vgrG2b)
Cytoplasmic
Cytoplasmic Membrane
Periplasmic
Outer Membrane
Extracellular
Unknown
Gene Feature Overview
| Strain |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (Stover et al., 2000)
GCF_000006765.1|latest |
| Locus Tag |
PA0262
|
| Name |
vgrG2b
|
| Replicon | chromosome |
| Genomic location | 293802 - 296861 (- strand) |
| Transposon Mutants | 13 transposon mutants in PAO1 |
| Transposon Mutants in orthologs | 10 transposon mutants in orthologs |
| Comment | Tli3 neutralizes the antibacterial activity of VgrG2b (PMID:31231326). |
| Comment | H2-T6SS evolved effector demonstrating antibacterial and anti-eukaryotic activity (trans-kingdom toxin) delivered into epithelial cells through the H2-T6SS machinery and VgrG2a (PA1511) |
| Comment | Required for Tle3 secretion, the C-Terminal domain of VgrG2b is antibacterial when delivered into the periplasm of prey bacteria (in the heterologous host E. coli) and its toxicity relies on an intact protease catalytic site (residus 932-941, PFAM04298) |
| Comment | The C-Terminal domain of VgrG2b interacts with the gamma-tubulin complex to promote a microtubule-dependant internalization of P. aeruginosa into non phagocytic cells (PMID:26037124) |
Cross-References
| RefSeq | NP_248953.1 |
| GI | 15595459 |
| Affymetrix | PA0262_at |
| Entrez | 881981 |
| GenBank | AAG03651.1 |
| INSDC | AAG03651.1 |
| NCBI Locus Tag | PA0262 |
| protein_id(GenBank) | gb|AAG03651.1|AE004464_4|gnl|PseudoCAP|PA0262 |
| TIGR | NTL03PA00263 |
| UniParc | UPI00000C4FCB |
| UniProtKB Acc | Q9I6M7 |
| UniProtKB ID | Q9I6M7_PSEAE |
| UniRef100 | UniRef100_Q9I6M7 |
| UniRef50 | UniRef50_Q9I3K1 |
| UniRef90 | UniRef90_Q9I3K1 |
Product
| Feature Type | CDS |
| Coding Frame | 1 |
| Product Name |
VgrG2b
|
| Synonyms | |
| Evidence for Translation |
Identified using nanoflow high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) in conjunction with microelectrospray ionization on LTQ XL mass spectrometer (PMID:24291602).
|
| Charge (pH 7) | -19.34 |
| Kyte-Doolittle Hydrophobicity Value | -0.478 |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 113.0 |
| Isoelectric Point (pI) | 6.16 |
Subcellular localization
| Individual Mappings | |
| Additional evidence for subcellular localization |
PDB 3D Structures
| Accession | Header | Accession Date | Compound | Source | Resolution | Method | Percent Identity |
| 6H56 | METAL BINDING PROTEIN | 07/23/18 | Effector domain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa VgrG2b | Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | 3.2 | X-RAY DIFFRACTION | 98.8 |
Pathogen Association Analysis
| Results |
Common
Found in both pathogen and nonpathogenic strains
Hits to this gene were found in 146 genera
|
Orthologs/Comparative Genomics
| Pseudomonas Ortholog Database | View orthologs at Pseudomonas Ortholog Database |
| Pseudomonas Ortholog Group |
POG000090 (3342 members) |
| Putative Inparalogs | None Found |
Interactions
| STRING database | Search for predicted protein-protein interactions using:
Search term: PA0262
Search term: vgrG2b
Search term: VgrG2b
|
Human Homologs
References
|
Rhs elements comprise three subfamilies which diverged prior to acquisition by Escherichia coli.
Wang YD, Zhao S, Hill CW
J Bacteriol 1998 Aug;180(16):4102-10
PubMed ID: 9696756
|
|
Type VI secretion system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: secretion and multimerization of VgrG proteins.
Hachani A, Lossi NS, Hamilton A, Jones C, Bleves S, Albesa-Jové D, Filloux A
J Biol Chem 2011 Apr 8;286(14):12317-27
PubMed ID: 21325275
|
|
Internalization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain PAO1 into Epithelial Cells Is Promoted by Interaction of a T6SS Effector with the Microtubule Network.
Sana TG, Baumann C, Merdes A, Soscia C, Rattei T, Hachani A, Jones C, Bennett KL, Filloux A, Superti-Furga G, Voulhoux R, Bleves S
mBio 2015 Jun 2;6(3):e00712
PubMed ID: 26037124
|
|
A Type VI Secretion System Trans-Kingdom Effector Is Required for the Delivery of a Novel Antibacterial Toxin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Berni B, Soscia C, Djermoun S, Ize B, Bleves S
Front Microbiol 2019;10:1218
PubMed ID: 31231326
|